Financial Ratio Analysis
Understanding Business Financial Position the Easy Way
Ratios compare two financial values, providing insights by breaking down complex elements into easily interpretable formats. This helps assess a company's revenue, liquidity, operational efficiency, and profitability. Ratio analysis is essential for financial analysis and management, making financial data more understandable for stakeholders. Financial statements alone may not fully inform stakeholders. Ratio analysis helps interpret these numbers, offering a clear view of a company's operations and health without requiring in-depth accounting knowledge.

Key Financial Ratios
Types Of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are categorized based on the specific aspect of a company's performance they measure. Here are the main types:
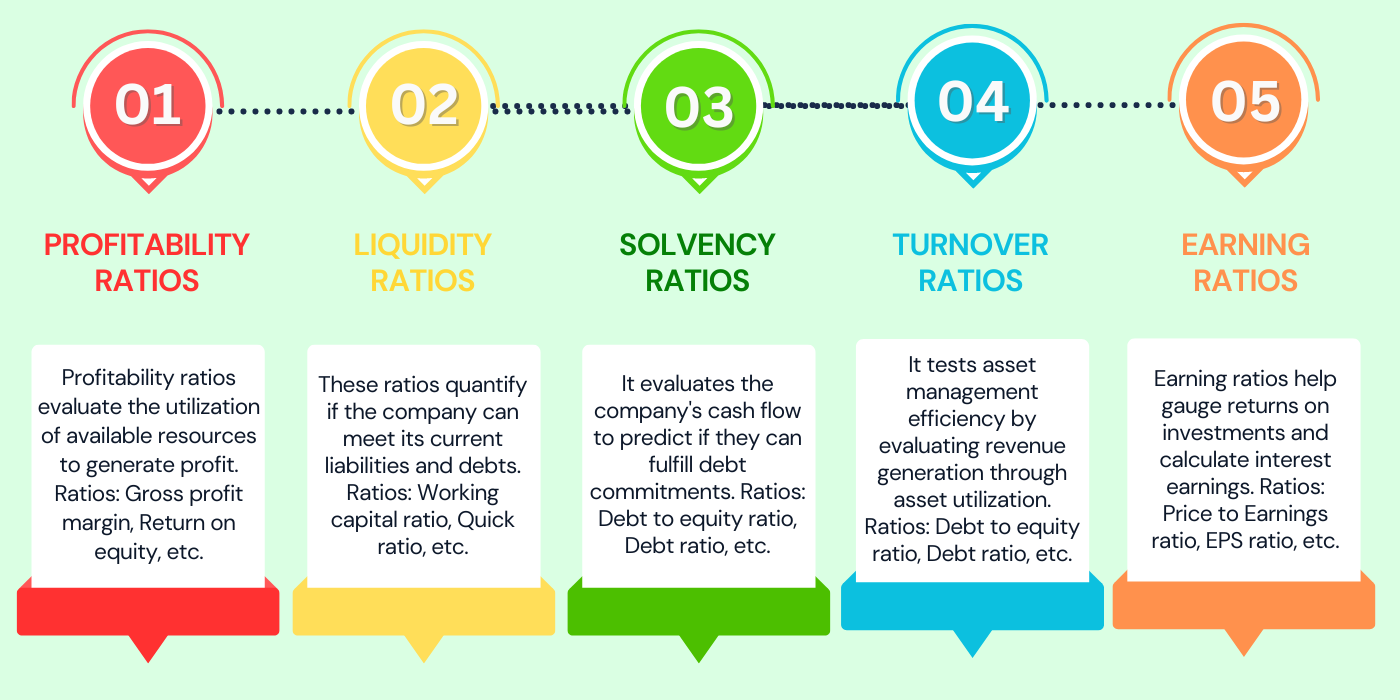
Profitability Ratios
This ratio compares your business's ability to generate revenue against its expenses, helping you determine a desired rate of return. It includes ratios such as:
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Operating Profit Ratio
- Net Profit Ratios
- Interest Coverage Ratio

Liquidity ratios
This ratio measures a company's ability to pay its debts on time. It is a crucial metric for determining a company's capacity to cover short-term obligations and manage cash flow. It includes ratios such as:
- Current Ratio
- Working Capital Ratio
- Quick Ratios etc.

Return On Investment Ratios
Return on Investment (ROI) or Return on Assets (ROA) measures the return generated relative to the investment cost, providing a broad indication of investment profitability. It includes ratios such as:
- Return on Equity
- Return on Assets

Efficiency Ratios Or Activity Ratio
This ratio measures how effectively a company utilizes its assets to generate income. It also indicates the time taken by a company to collect cash from customers or convert inventory into cash through sales. These ratios are used by both the company and its stakeholders, including investors and creditors, to assess profitability and make comparisons. It includes ratios such as:
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Accounts Receivable Ratio
- Accounts Receivable Days
- Accounts Payable Ratio
- Cash Turnover

Solvency Ratios& Leverage Ratios
It measures your business’s ability to make payments and settle its long-term obligations to creditors. A balanced ratio indicates a more creditworthy and financially sound company in the long term. It includes ratios such as:
- Debt to Equity
- Debt to Capital
- Debt to Tangible Net Worth
- Total Liabilities to Equity
- Total Assets to Equity
- Debt to EBITDA

Market Ratios
These ratios help understand the financial health of a publicly traded company's stock. They reveal the relationship between the company's share price and its earnings, growth, and assets, indicating the company's value. It includes ratios such as:
- Dividend Yield
- Earnings Per Share
- Price Earnings Ratio

Classification of Ratio Analysis
Advantages Of Accounting Ratios
Accounting ratios offer several advantages in evaluating the financial health and performance of a business:

Simplification Of Complex Data
Ratios condense complex financial information into simple, understandable metrics, making it easier for stakeholders to interpret and analyze.

Measure Trends
Ratios help measure trends by comparing current performance with past records, providing insights into the movement of company operations over time. This analysis helps monitor and identify issues that can be highlighted and resolved promptly.

Benchmarking
Ratios enable businesses to benchmark their performance against industry averages or leaders. This comparison helps identify whether a company is performing better or worse than its peers in key financial areas.

Forecasting And Planning
By analyzing historical ratios and trends, stakeholders can forecast future financial performance and plan strategies accordingly.